Examples Of Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
There are in fact no purely ionic bonds just as there are no purely covalent bonds. For example tetrachloro-methane carbon tetrachloride CCl 4 has polar CCl bonds but the tetrahedral arrangement of the four bonds about the central carbon atom causes the individual bond moments to cancel.

Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Covalent Bonding Chemistry Lessons Molecules
However there are different levels of covalent bonding.

Examples of nonpolar covalent bonds. Using the periodic table of electronegativities from the last page write down examples of atom pairs which you would expect to form covalent bonds polar covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Examples of homonuclear nonpolar molecules are oxygen O 2 nitrogen N 2 and ozone O 3. Covalent bonds are much more common in organic chemistry than ionic bonds.
NONPOLAR COVALENT BONDS H2 or Cl2 2. The chemical energy released in the formation of non-covalent interactions is typically on the order of 15 kcalmol 10005000 calories per 602 10 23 molecules. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atomsThese electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding.
Most carbon compounds are nonpolar. A covalent bond consists of the simultaneous attraction of two nuclei for one or more pairs of electrons. However a molecule may be polar or nonpolar depending on its geometry.
Covalent bonds occur between identical atoms or between different atoms whose. Electronegativity is probably the most important concept to understand in organic chemistry were going to use the definition that Linus Pauling gives in his book the nature of the chemical bond so Linus Pauling says that electronegativity refers to the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself so if I look at a molecule Im going to compare two atoms in that molecule Im. For many molecules the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence.
A non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons but rather involves more dispersed variations of electromagnetic interactions between molecules or within a molecule. Oxygen Atom Oxygen Atom Oxygen Molecule O2 POLAR COVALENT BONDS H2O. When elements combine there are two types of bonds that may form between them.
Covalent bonds- Two atoms share one or more pairs of outer-shell electrons. Nonpolar Molecule Examples. The bonding electrons in polar covalent bonds are not shared equally and a bond moment results.
Thus as the electronegativity difference of the two bonded elements increases a nonpolar bond gives way to a polar bond which in turn becomes an ionic bond. The Na becomes Na and the Cl becomes Cl- charged particles or ions. Covalent bonds between identical atoms as in H 2 are nonpolarie electrically uniformwhile those between unlike atoms are polarie one atom is slightly negatively charged and the other is slightly positively charged.
Other nonpolar molecules include carbon dioxide CO 2 and the organic molecules methane CH 4 toluene and gasoline. A notable exception is carbon monoxide CO. Tics of BOTH ionic and covalent bonding.
Electronega-tivity differences determine the balance of character. This partial ionic character of covalent bonds increases with the difference in the electronegativities of the two. Covalent bonds result from a sharing of electrons by two or more atoms usually nonmetals.
The electrons located between the two nuclei are bonding electrons. Bonding is a continuum of types. Lewis theory Gilbert Newton Lewis 1875-1946 focuses on the valence electrons since.
Examples of compounds containing these bonds include methane water and carbon dioxide. Ionic bonds result from a transfer of electrons from one species usually a metal to another usually a nonmetal or polyatomic ion. Carbon can form nonpolar covalent pure covalent bonds when it bonds to itself as in graphene and diamond.

About The Mcat Mcat Chemistry Chemical Reactions Ciencias Quimica Quimica Cine En Casa

Bonding Learning Activities Distance Learning Chemistry Activities Common Core Reading Writing Standards

Covalent Bond Examples Covalent Bonding Electron Affinity Electron Configuration

Definition And Examples Of A Polar Bond In Chemistry Covalent Bonding Chemical Bond Chemistry

Hf Is Polar Or Nonpolar Covalent Bond Covalent Bonding Polar Molecules

Difference Between Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

Infographic Defining Bonds As Electronegativity Differences En Intermolecular Force Chemistry Linus Pauling

Polar Covalent Bonds Covalent Bonding Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Help

Nonpolar Covalent Bond Examples Covalent Bonding Bond Mario Characters

Polar Vs Nonpolar Covalent Bonding Medical Student Study Science Chemistry

Why Is Water A Polar Molecule Water Molecule Polarity Of Water Covalent Bonding

Biology Polar Vs Nonpolar Bonds Expii Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Quotes Chemistry Education

Polar And Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Definitions And Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Chemistry Intermolecular Forces Polar Bonds And Polarity Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Education
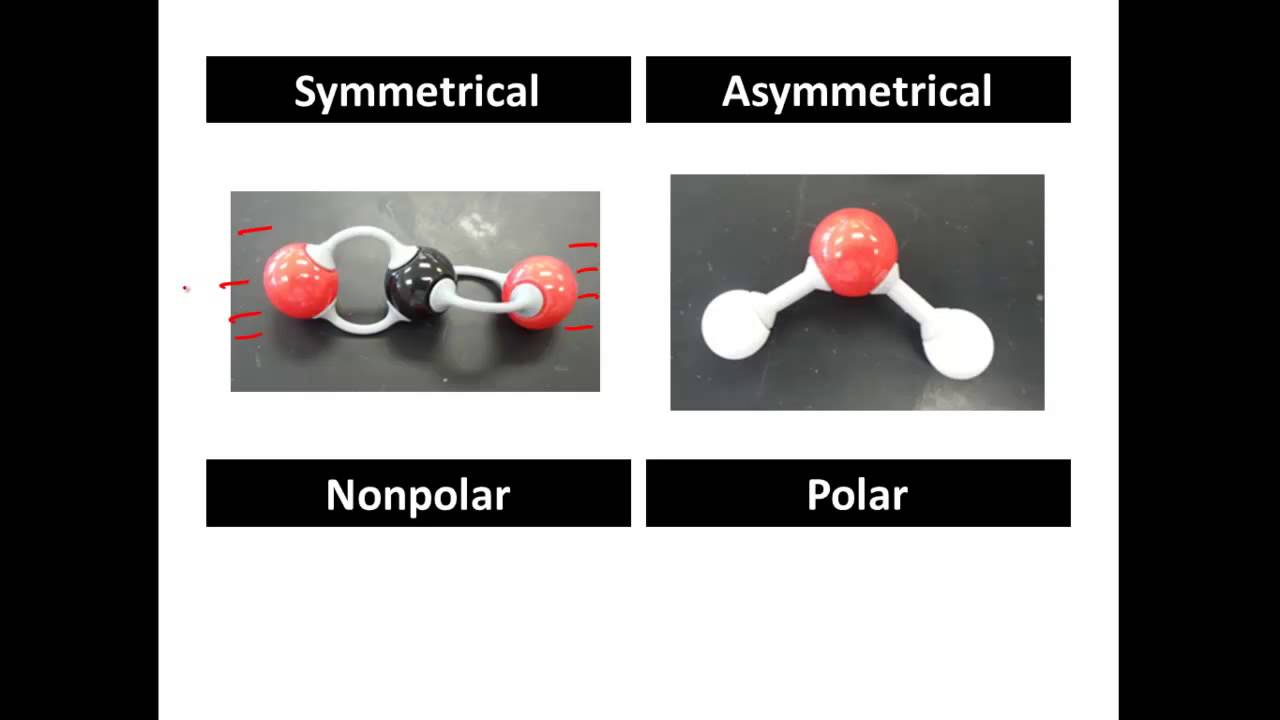
Polar And Non Polar Covalent Molecules Polar Vs Nonpolar Youtube Playlist Science Chemistry Molecules Chemistry

Details Here Https Dantuckerautos Com Fresh Protons In Carbon Covalent Bonding Polar Graphics Design Ideas

Four Covalent Bonds Carbon Has Four Valence Electrons And Here A Valence Of Four Each Hydrogen Atom Has One Vale Covalent Bonding Chemical Bond Ionic Bonding

Difference Between Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Definition Formation Properties Examples Covalent Bonding Study Chemistry Chemical Bond
